🤖 讓變數學會七十二變的高手~運算子
運算子
程式的世界中,變數是無時無刻一直在變化的,
變數的變化
但為甚麼變
原來一切都
算術運
- 在程式之,並將這兩個物件在指定的運算
C#之中
| 運算子 | 別 |
|---|---|
| + | 元 |
| - | 元 |
| * | 元 |
| / | 元 |
| % | 元 |
範例:使,來算出今天禮拜幾
using Syste
using Syste;
using Syste
using Syste
using Syste
namespace C
{
class P
{
sta] args)
{
公式
m + 3 * (m + 1) / 5 + y + y / 4 - y / 7;
021/9/6 星期" + week);
}
}
}
結果:
2021/9/6
在這公式中運算子,也體會到C#讓人十分驚豔的運算
特別的
- 在 C#中的所差異
- 在整數的動被捨去
範例:試我們觀念中應該答案是 1.5
using Syste
using Syste;
using Syste
using Syste
using Syste
namespace C
{
class P
{
sta] args)
{
ns : " + ans);
}
}
}
結果:
Ans : 1
- 由上我們後會直接被
向0無條件捨去 - 除非做浮浮點數
範例:驗數變數與直接做浮點數除法的差異
using Syste
using Syste;
using Syste
using Syste
using Syste
namespace C
{
class P
{
sta] args)
{
給浮點數變數
= " + x + " ,y = " + y);
}
}
}
結果
x = 4 ,y
餘數運
- 使用此運數
- 與方法[Macs.microsoft.com/zh-tw/dotnet/api/system.math.divrem一樣的結果
範例:我 來看看他們的餘數分別是多少
using Syste
using Syste;
using Syste
using Syste
using Syste
namespace C
{
class P
{
sta] args)
{
餘運算
0 % 4 =" + no20);
1 % 4 =" + no21);
2 % 4 =" + no22);
3 % 4 =" + no23);
4 % 4 =" + no24);
5 % 4 =" + no25);
}
}
}
結果:
20 % 4 =0 21 % 4 =1 22 % 4 =2 23 % 4 =3 24 % 4 =0 25 % 4 =1
方法(Math)
- C#也有提供我們很多數學方法
- 我們來介紹幾個比較常用的方法
| 功能 | 方法 | 範例 | 數學表示 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乘冪 | Math.Pow() | Math.Pow(2,3) | 2^3 | ||
| 平方根 | Math.Sqrt() | Math.Sqrt(4) | √4 | ||
| 絕對值 | Math.Abs() | Math.Abs(-4) | ` | -4 | ` |
- 另外方法中還為我們定義三個欄位
| 數學涵義 | 程式表示 | 近似值 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|---|
τ | Math.Tau | 6.2831853071795862 | 弧度 |
π | Math.PI | 3.1415926535897931 | 圓周率 |
e | Math.E | 2.7182818284590451 | 自然對數底數 |
隨堂小練習
題目:已知梯形面積公式為((上底+下底)X 高/2),目前知道上底是 30,下底是 52,高為 46
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CsharpDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//宣告上底
int x = 30;
//宣告下底
int y = 52;
//宣告高
int z = 46;
//進行計算
int ans = (x + y) * z / 2;
//印出答案
Console.WriteLine("Ans : " + ans);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
結果:
Ans : 1886
遞增運算子~++
- 他是屬於一元運算子
- 增加的量為 1
範例 1(後置遞增運算子):我們來算算我今年 48 歲,明年我幾歲?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CsharpDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//宣告我今年48歲
int age = 48;
Console.WriteLine("我今年" + age + "歲");
//使用後置遞增運算子,計算明年年紀
age++;
Console.WriteLine("我明年" + age + "歲");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
結果:
我今年 48 歲 我明年 49 歲
範例 2(前置遞增運算子):我們來比較看看前置跟後置的差異吧
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CsharpDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//後置遞增運算子,印出它的變化過程
Console.WriteLine("--後置運算子--");
int x = 1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(x++);
Console.WriteLine(x);
//前置遞增運算子,印出它的變化過程
Console.WriteLine("--前置運算子--");
int y = 1;
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.WriteLine(++y);
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
結果:
--後置運算子-- 1 1 2 --前置運算子-- 1 2 2
由此我們可以看到前置跟後置的差異會是,在運算「之後」或「之前」某數的值
既然有遞增那必然有遞減運算子~--
範例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CsharpDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//遞減運算子
int x = 5;
//後置
Console.WriteLine(x--);
//前置
Console.WriteLine(--x);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
結果:
5 3
大家可能會覺得,這結果也太奇怪了吧?! 為什麼不是 5,4 呢? 原因很簡單,因為我們先用後置遞減運算子,所以他是在輸出 5 之後,x 變成 4 了, 接下來使用前置遞減運算子,所以 4 先被減成 3,然後才輸出
指派運算子
| 功能 | 範例 | 等值寫法 | 類別 |
|---|---|---|---|
+= | x += 100 | x = x + 100 | 二元 |
-= | x -= 100 | x = x - 100 | 二元 |
*= | x *= 100 | x = x * 100 | 二元 |
/= | x /= 100 | x = x / 100 | 二元 |
%= | x %= 100 | x = x % 100 | 二元 |
範例:來試試看加法指派運算子 +=
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CsharpDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//加法指派運算子 += (整數版)
Console.WriteLine("--整數版--");
int x = 10;
x += 100;
Console.WriteLine(x);
//加法指派運算子 += (字串版)
Console.WriteLine("--字串版--");
string name = "孤獨一隻雞";
name += " 史上最帥!";
Console.WriteLine(name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
結果:
--整數版-- 110 --字串版-- 孤獨一隻雞 史上最帥!
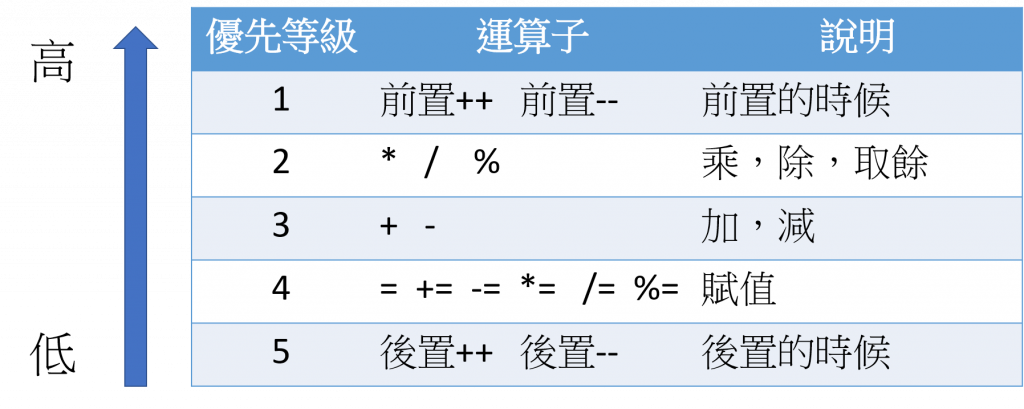
優先等級
- 小時候學數學時,常常會說先乘除後加減,但這麼多運算子中到底優先順序是什麼呢?
- 雖然有優先順序這東西,但實際上程式撰寫時,還是建議各位搭配
()做使用,這樣能增加程式的可讀性